A critical network infrastructure has encountered significant operational disruptions, leading to system outages and compromised machines. Public message boards displayed politically charged messages, and several systems were wiped, causing widespread service failures. Initial investigations reveal that attackers compromised the Active Directory (AD) system and deployed wiper malware across multiple machines.
Fortunately, during the attack, an alert employee noticed suspicious activity and immediately powered down several key systems, preventing the malware from completing its wipe across the entire network. However, the damage has already been done, and your team has been tasked with investigating the extent of the compromise.
You have been provided with forensic artifacts collected via KAPE SANS Triage from one of the affected machines to determine how the attackers gained access, the scope of the malware's deployment, and what critical systems or data were impacted before the shutdown.
Category: Endpoint Forensics
Tools: Registry Explorer Event Log Explorer NTFS Log Tracker MFTECmd VirusTotal
Q1: The attack began with using a Group Policy Object (GPO) to execute a malicious batch file. What is the name of the malicious GPO responsible for initiating the attack by running a script?

The scenario already telling us that We have been provided with forensic artifacts collected via KAPE SANS Triage so my go-to tools for this lab are gonna be Eric Zimmerman's Tools.
One thing I learned when its come to any Windows forensics lab is always looking for Sysmon log first then Event ID 4688 from Security log as an alternative for a quick win as we can see that we have Sysmon available on this lab right here.
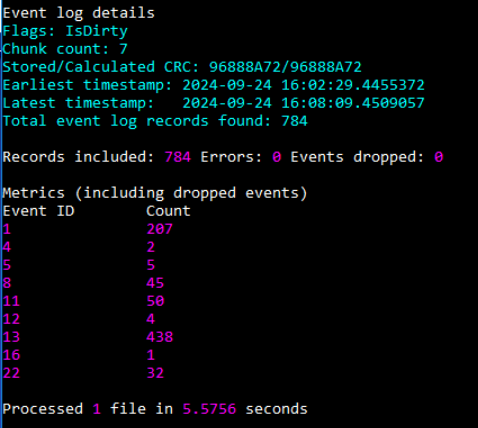
Then I used EvtxECmd to parse Sysmon log file into sysmon.csv file and EvtxECmd shown that we have total of 784 events from this log and the timestamp of earliest record and latest record is only 5-6 minutes which is not a lot to unpack here.
Command: EvtxECmd.exe -f "C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Start Here\Artifacts\C\Windows\System32\winevt\logs\Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon%4Operational.evtx" --csv output --csvf sysmon.csv
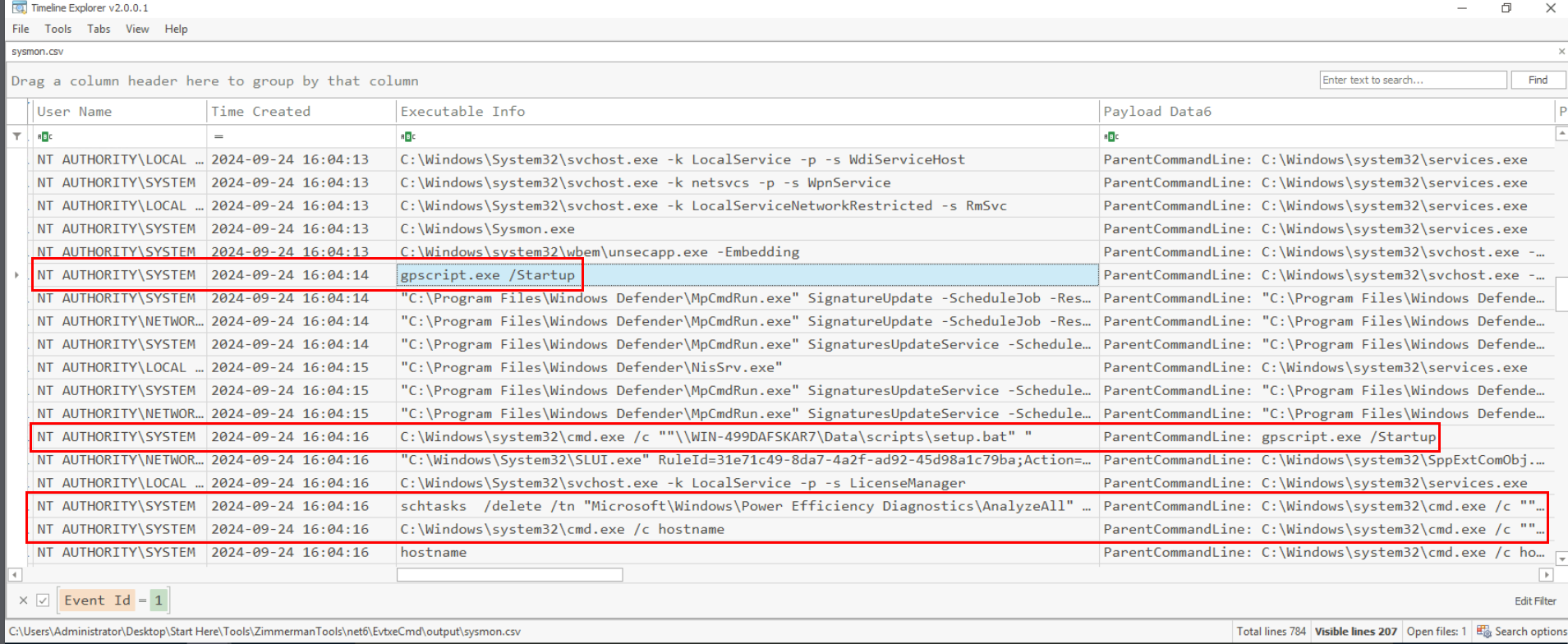
Then I opened the output file with Timeline Explorer, filter with Event ID 1 and then we can see that group policy was used to execute setup.bat script and started the whole chain of execution.
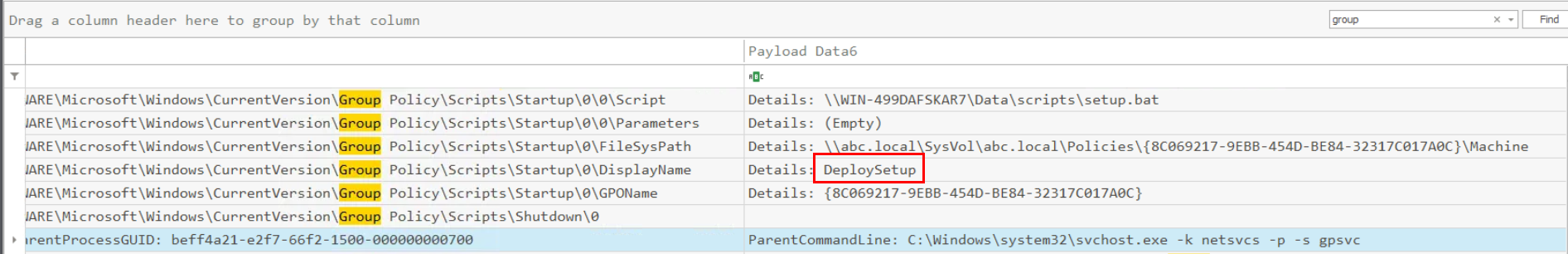
We can remove filter and just simply search for "Group" for any records which this word which we will see that name of GPO that was used to execute immediate task right here.
DeploySetup
Q2: During the investigation, a specific file containing critical components necessary for the later stages of the attack was found on the system. This file, expanded using a built-in tool, played a crucial role in staging the malware. What is the name of the file, and where was it located on the system? Please provide the full file path.
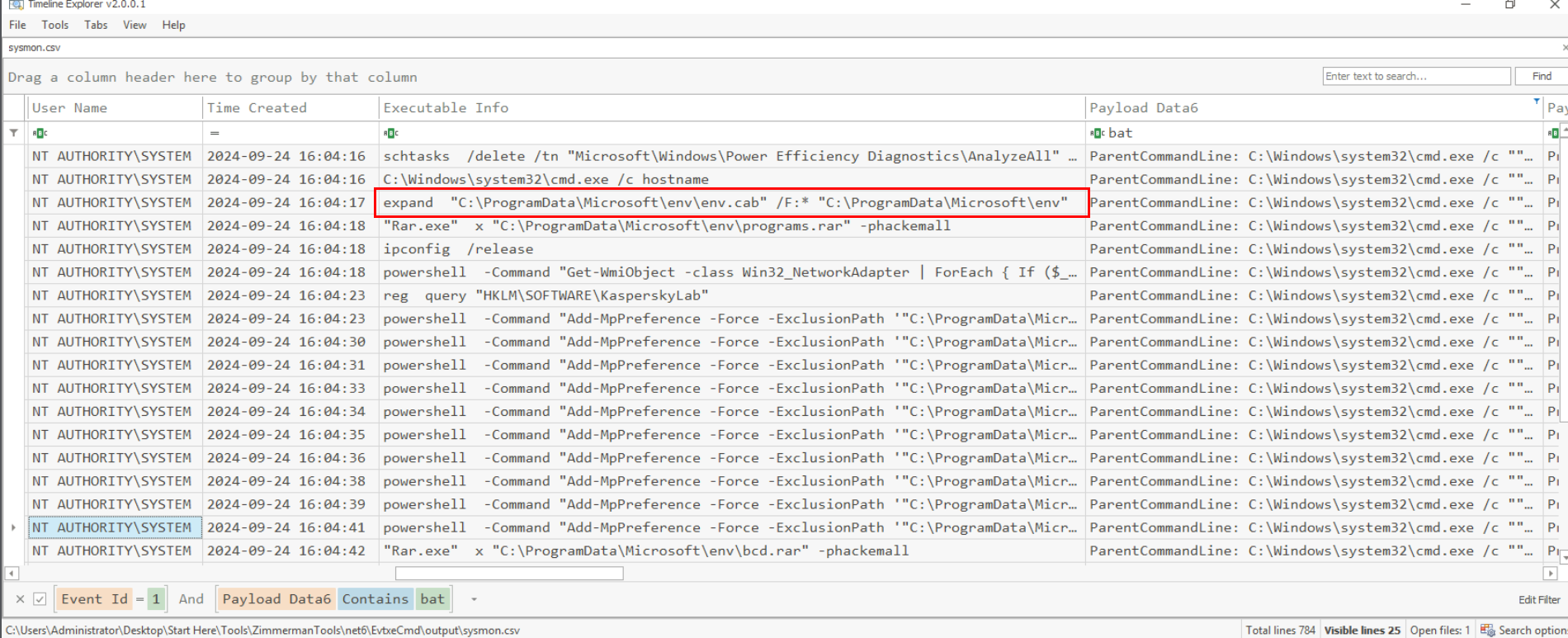
Going back to Event ID 1 then we can filter for the parent process command line that contain the word "setup.bat" to find child processes spawned under this process and it reveals that its started my delete "AnalyzeAll" schedule task, query hostname and then extract the content of env.cab file to C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\env.
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\env\env.cab
Q3: The attacker employed password-protected archives to conceal malicious files, making it important to uncover the password used for extraction. Identifying this password is key to accessing the contents and analyzing the attack further. What is the password used to extract the malicious files?
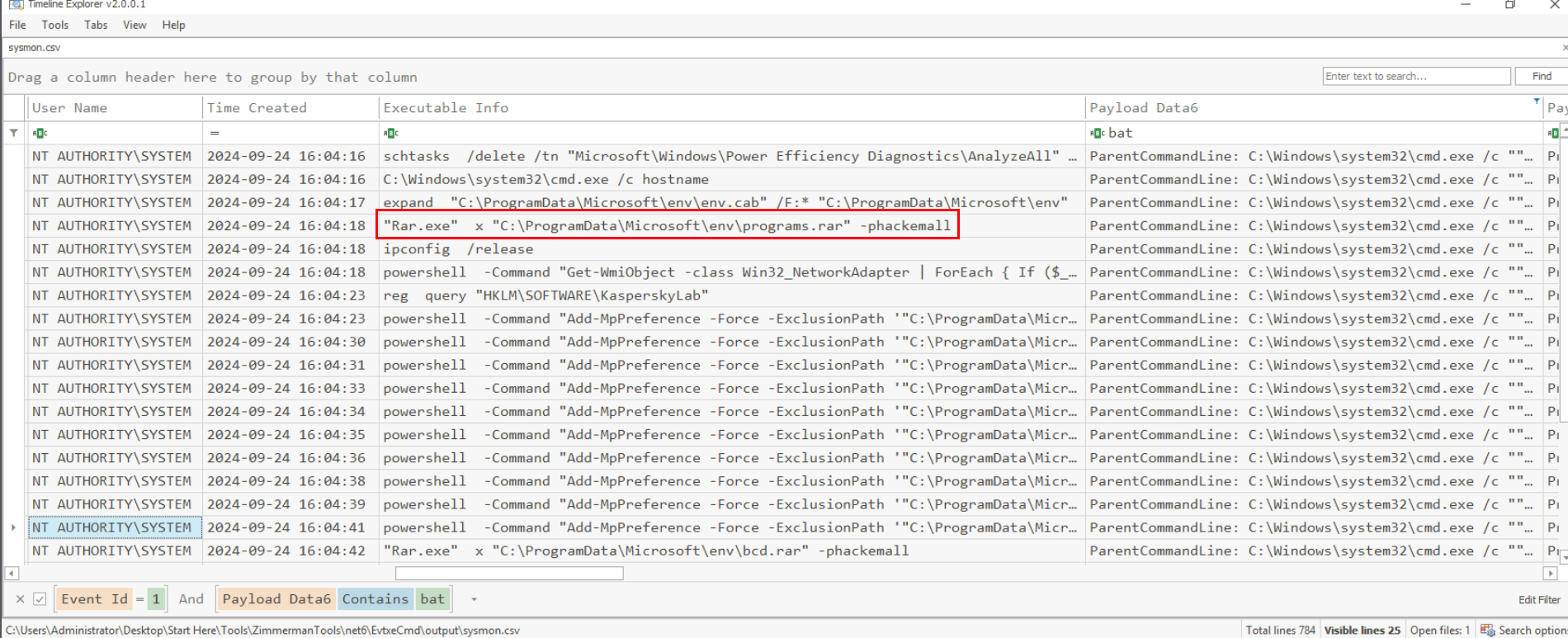
And then it extracted the content of programs.rar that was zipped with password "hackemall", release current IP address of the computer and use WMI to query for other network adapter, query for the installation of Kaspersky product.
hackemall
Q4: Several commands were executed to add exclusions to Windows Defender, preventing it from scanning specific files. This behavior is commonly used by attackers to ensure that malicious files are not detected by the system's built-in antivirus. Tracking these exclusion commands is crucial for identifying which files have been protected from antivirus scans. What is the name of the first file added to the Windows Defender exclusion list?
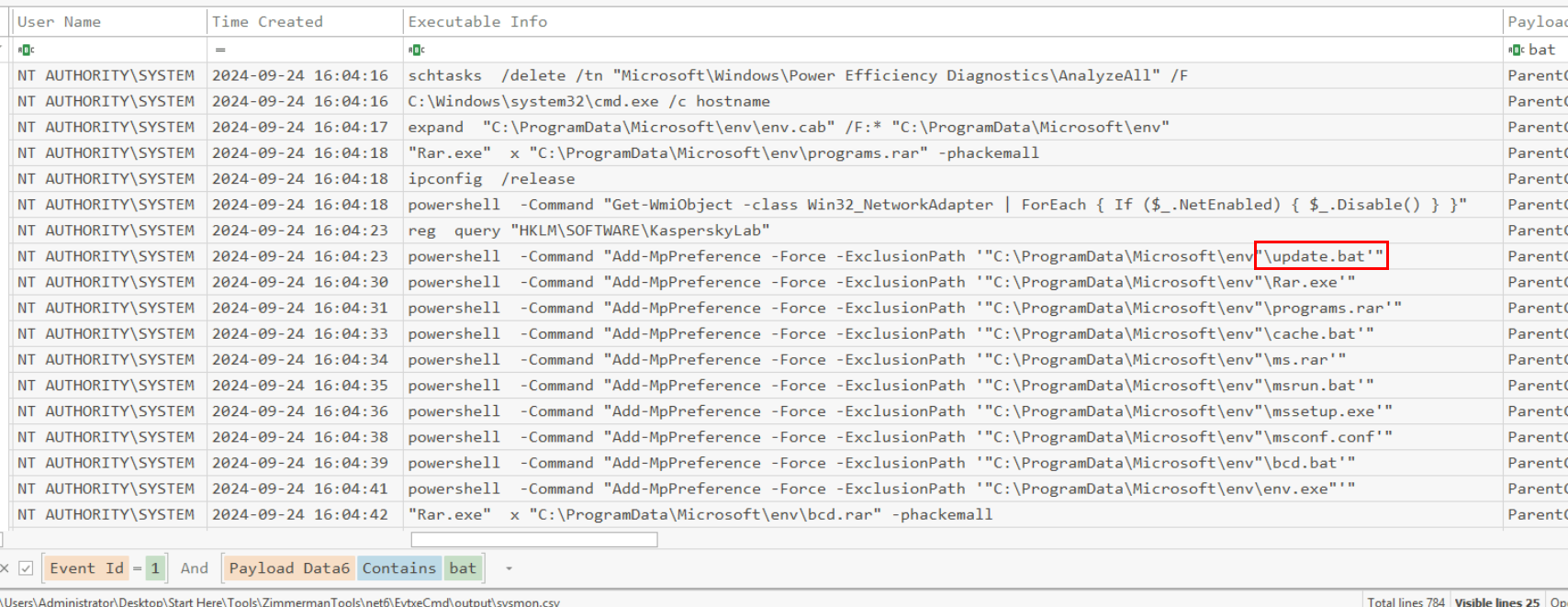
It proceeds to create Defender exclusion for 10 files located on C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\env which is the extracted location of env.cab. the first file that was excluded is the update.bat file here.
update.bat
Q5: A scheduled task has been configured to execute a file after a set delay. Understanding this delay is important for investigating the timing of potential malicious activity. How many seconds after the task creation time is it scheduled to run?
Note: Consider the system's time zone when answering questions related to time.
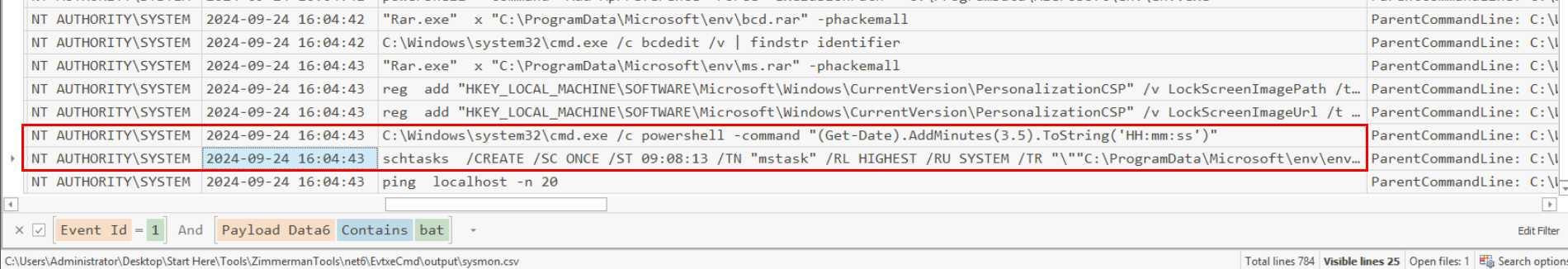
It proceed to extract 2 more rar files and use bcdedit with /v for verbose mode and get the entry identifiers of all boot configurations, add images to LockScreen and then get the local timestamp + 3.5 minutes for the schedule task creation. so now we know that it took 3.5 minutes from local time to create schedule task then out formula to convert into second is
3.5 minutes = ( 60 seconds * 3 ) + (60 seconds * 1/2) = 210 seconds
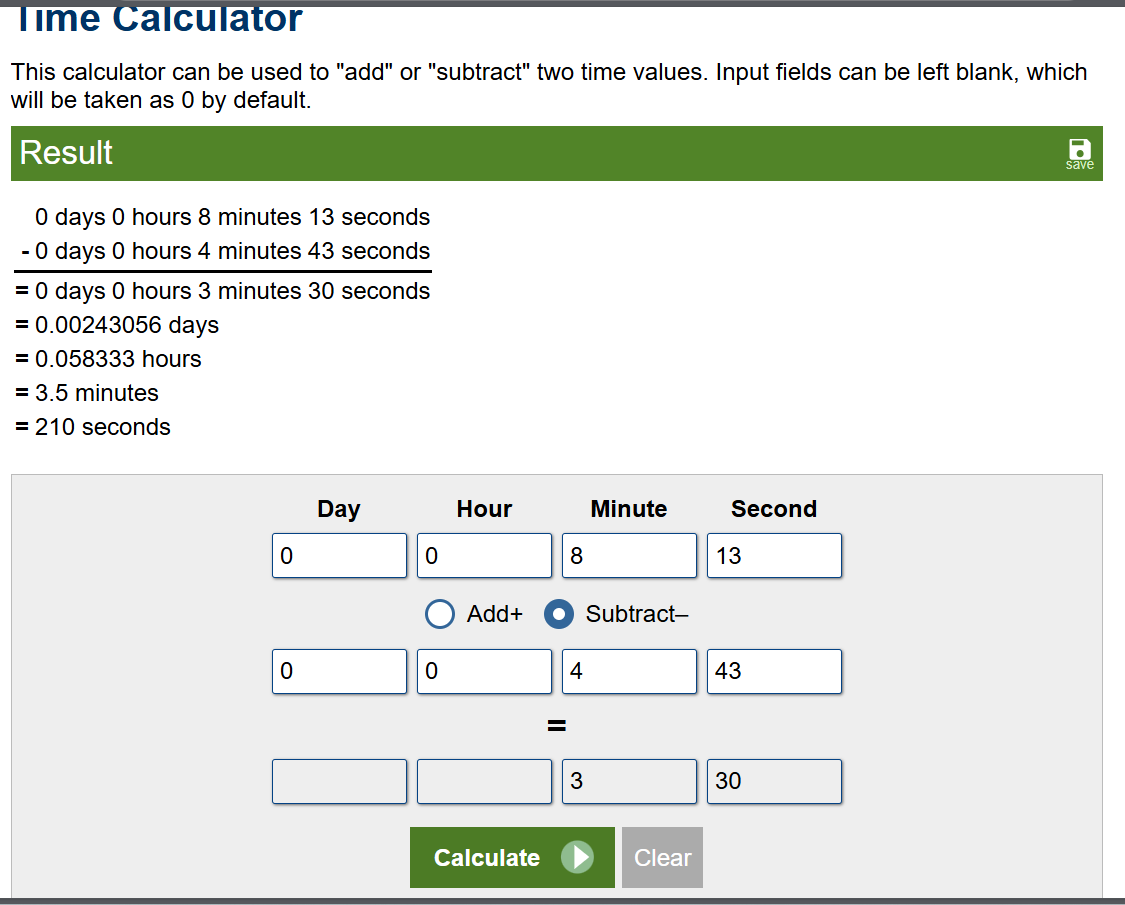
Alternatively, we can use time calculator as well.
210
Q6: After the malware execution, the
wmicutility was used to unjoin the computer system from a domain or workgroup. Tracking this operation is essential for identifying system reconfigurations or unauthorized changes. What is the Process ID (PID) of the utility responsible for performing this action?
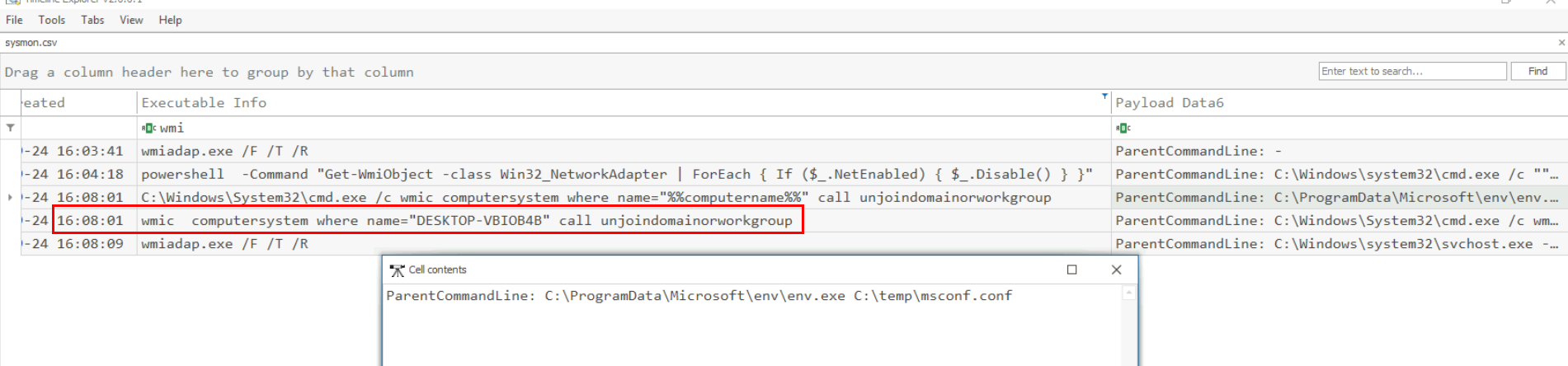
We can search for "wmic" binary for any WMI operation which reveals that at 16:08:01 UTC, the child process of env.exe that was configured to run at 09:08:13 local time just started a child process to unjoin "DESKTOP-VBIOB4B" from the domain.
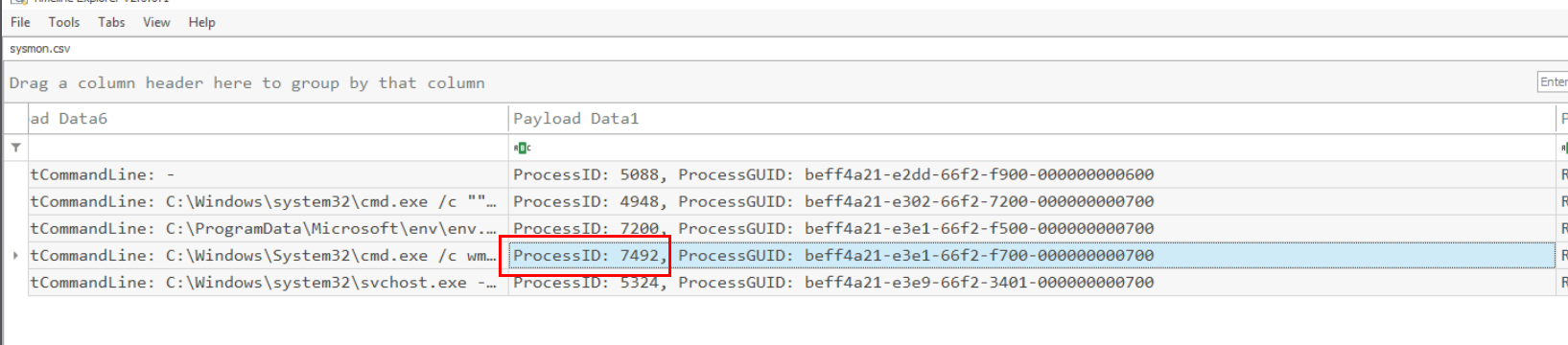
We can get the process ID of this utility right here.
7492
Q7: The malware executed a command to delete the
Windows Boot Manager, a critical component responsible for loading the operating system during startup. This action can render the system unbootable, leading to serious operational disruptions and making recovery more difficult. What command did the malware use to delete the Windows Boot Manager?
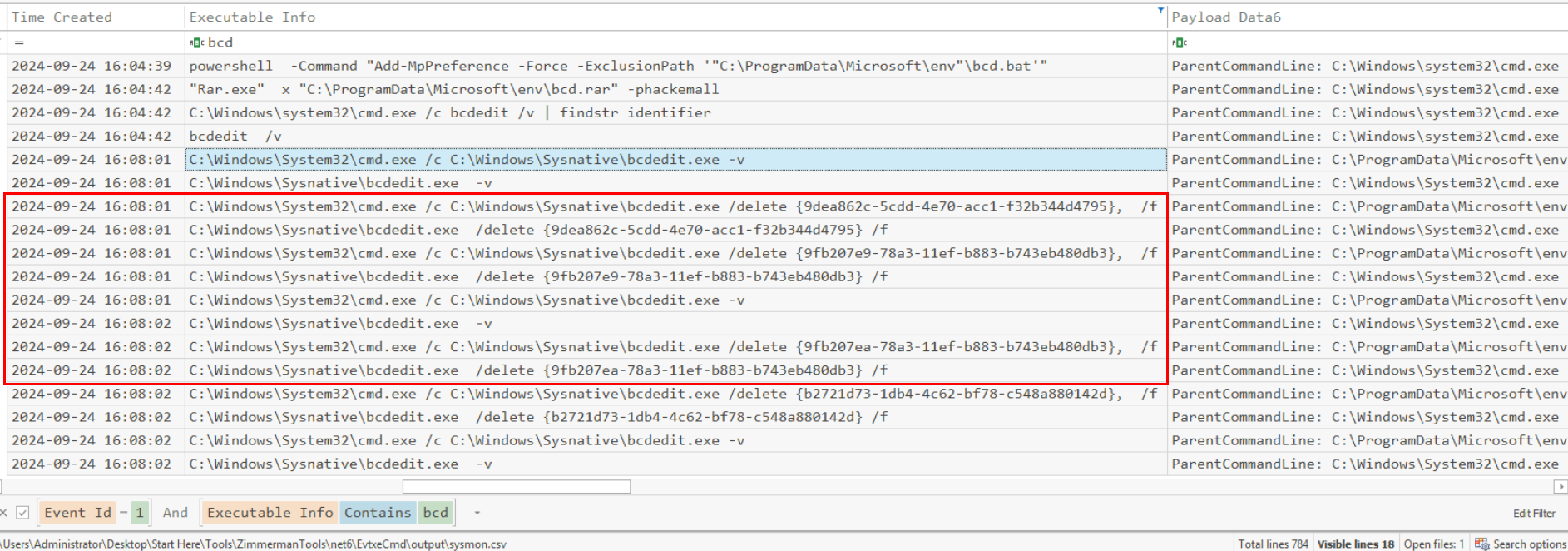
We know that bcedit /v was used to find entry identifiers of all boot configurations then after simply search for the usage of this binary again then we can see that env.exe spawned these processes to delete Windows Boot Manager indicates by the well-known GUID of it right here.
C:\Windows\Sysnative\bcdedit.exe /delete {9dea862c-5cdd-4e70-acc1-f32b344d4795} /f
Q8: The malware created a scheduled task to ensure persistence and maintain control over the compromised system. This task is configured to run with elevated privileges every time the system starts, ensuring the malware continues to execute. What is the name of the scheduled task created by the malware to maintain persistence?
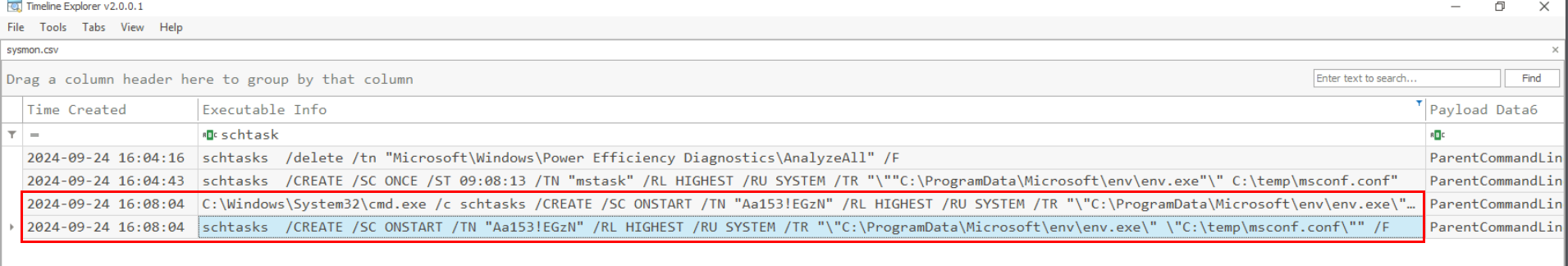
Beside the first schedule task that was created to run env.exe just one, the other schedule task was also created to run as SYSTEM on every startup and it was set to run env.exe.
Aa153!EGzN
Q9: A malicious program was used to lock the screen, preventing users from accessing the system. Investigating this malware is important to identify its behavior and mitigate its impact. What is the name of this malware? (not the filename)
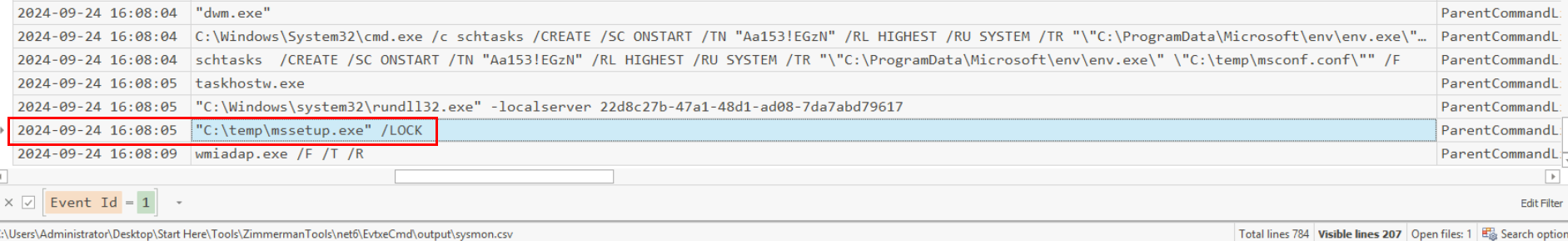
This time, I removed most of filter and focus on last trail of the process execution which I found the mssetup.exe was executed with /LOCK argument, indicates that it was executed to lock something and maybe its the screen.
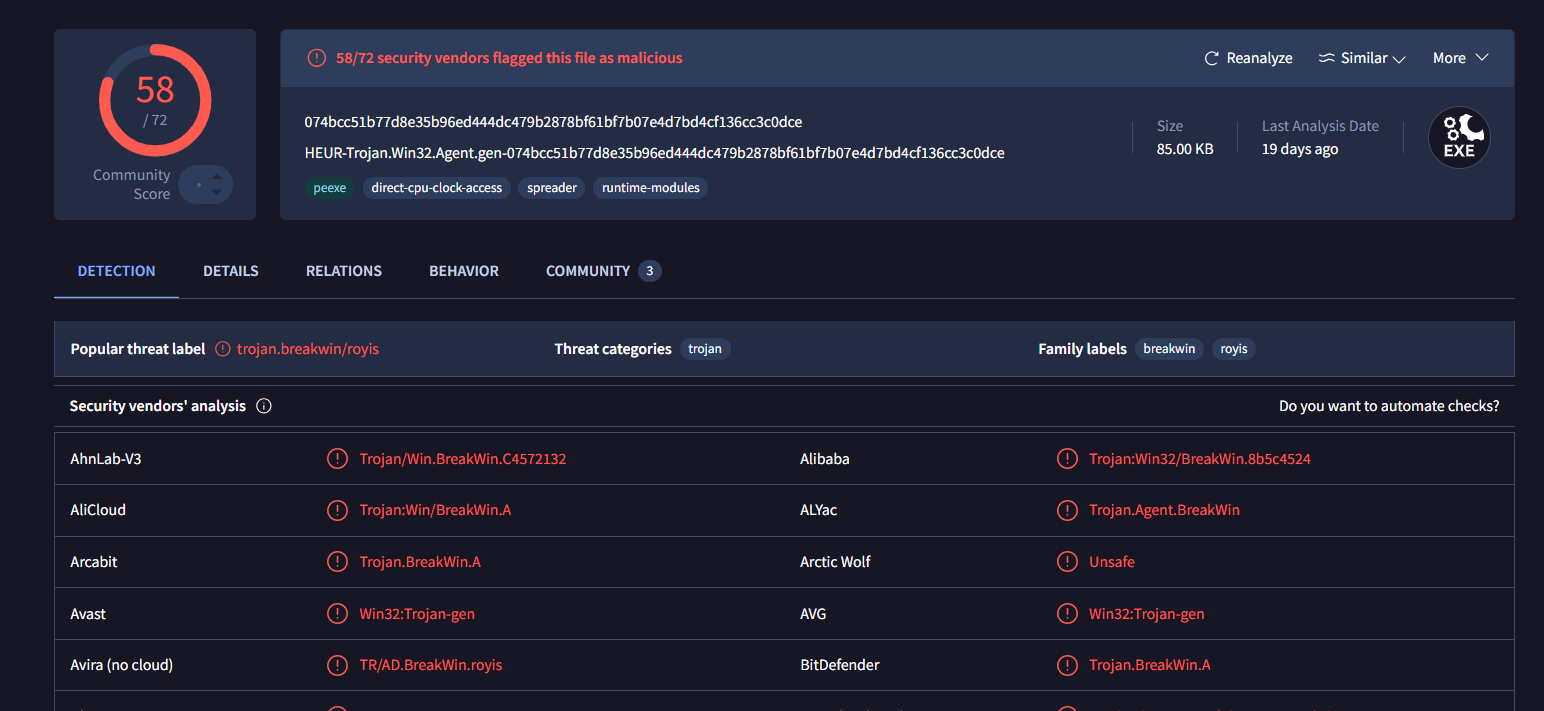
I searched its MD5/SHA256 on VirusTotal which reveals the family of this malware and it is the answer of this question.
BreakWin
Q10: The disk shows a pattern where malware overwrites data (potentially with zero-bytes) and then deletes it, a behavior commonly linked to Wiper malware activity. The USN (Update Sequence Number) is vital for tracking filesystem changes on an NTFS volume, enabling investigators to trace when files are created, modified, or deleted, even if they are no longer present. This is critical for building a timeline of file activity and detecting potential tampering. What is the USN associated with the deletion of the file
msuser.reg?
To find out about this, we need to use NTFS Log Tracker to parse UsnJournal log to get USN.
After specified UsnJournal and $LogFile path, I have to create sqlite db before start parsing process.
We can use "Search" function to find the existence of msuser.reg here but I love using Timeline Explorer more so I exported them to CSV.
Now its time to open NLT_UsnJnrl file right here.
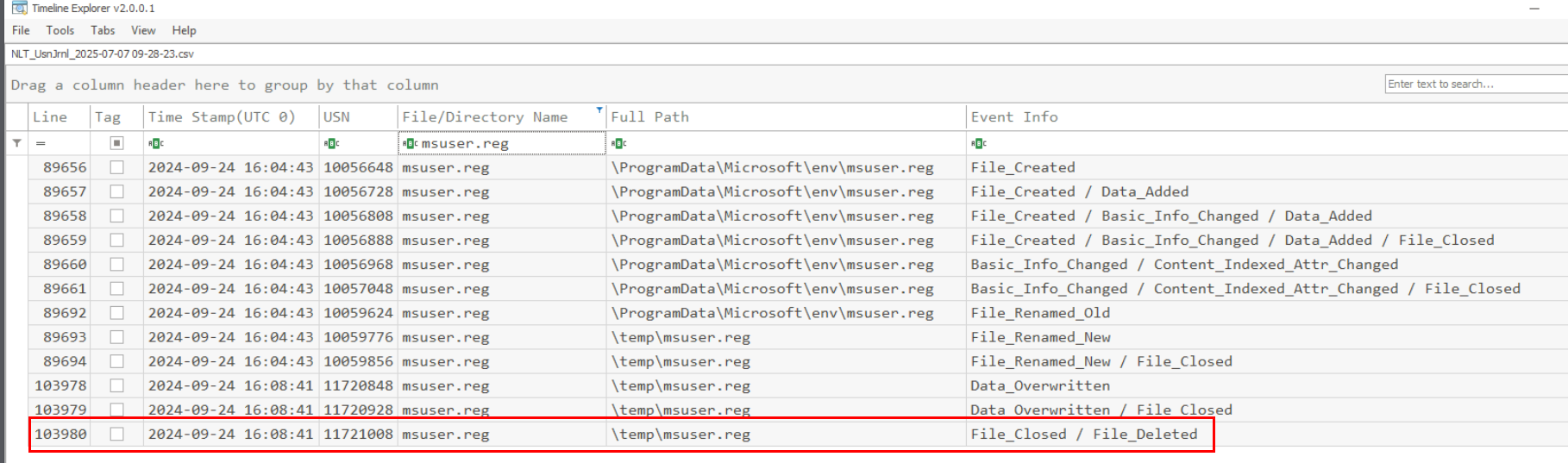
Filter with the filename and then we will have the USN associate with the file deletion at the end of this record right here.
11721008
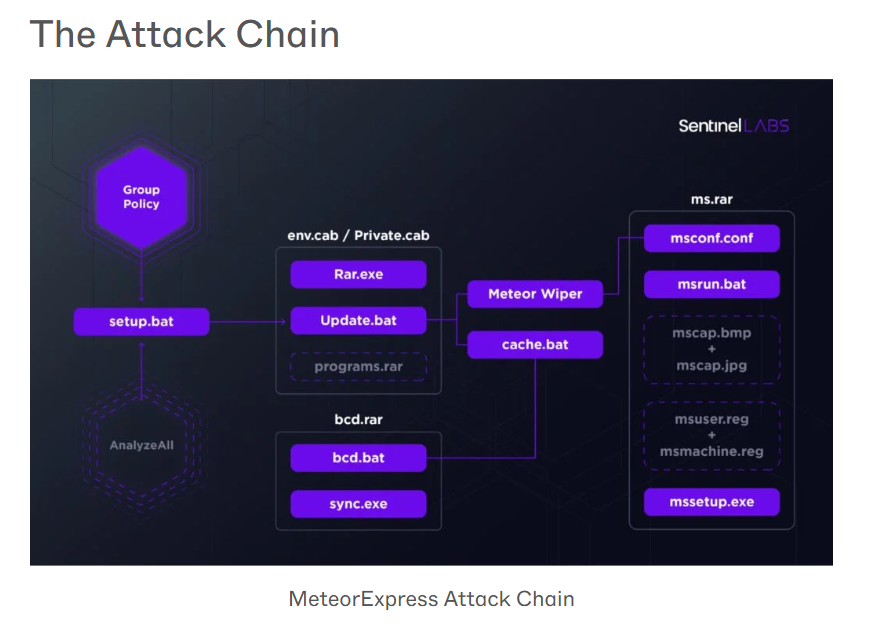
After conduct some searching on What is Breakwin malware, I've come across the SentinelLabs blog post that is obviously the main inspiration of this lab since all of the process chain (attack chain) are the same including the name like it was bit-to-bit copy of this incident.

The article is called "MeteorExpress | Mysterious Wiper Paralyzes Iranian Trains with Epic Troll" which covers most of the apperance of the incident and everything we need to know including the technical details when the setup.bat script was executed til the end of the chain so if you have time then give it a read then you will understand the whole attack chain and the intention behind this incident.
https://cyberdefenders.org/blueteam-ctf-challenges/achievements/Chicken_0248/meteorhit/